DMARC Now Mandatory
By February 2024, any company sending more than 5,000 email messages through Google or Yahoo will have to start using an authentication technology known as Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance (DMARC).
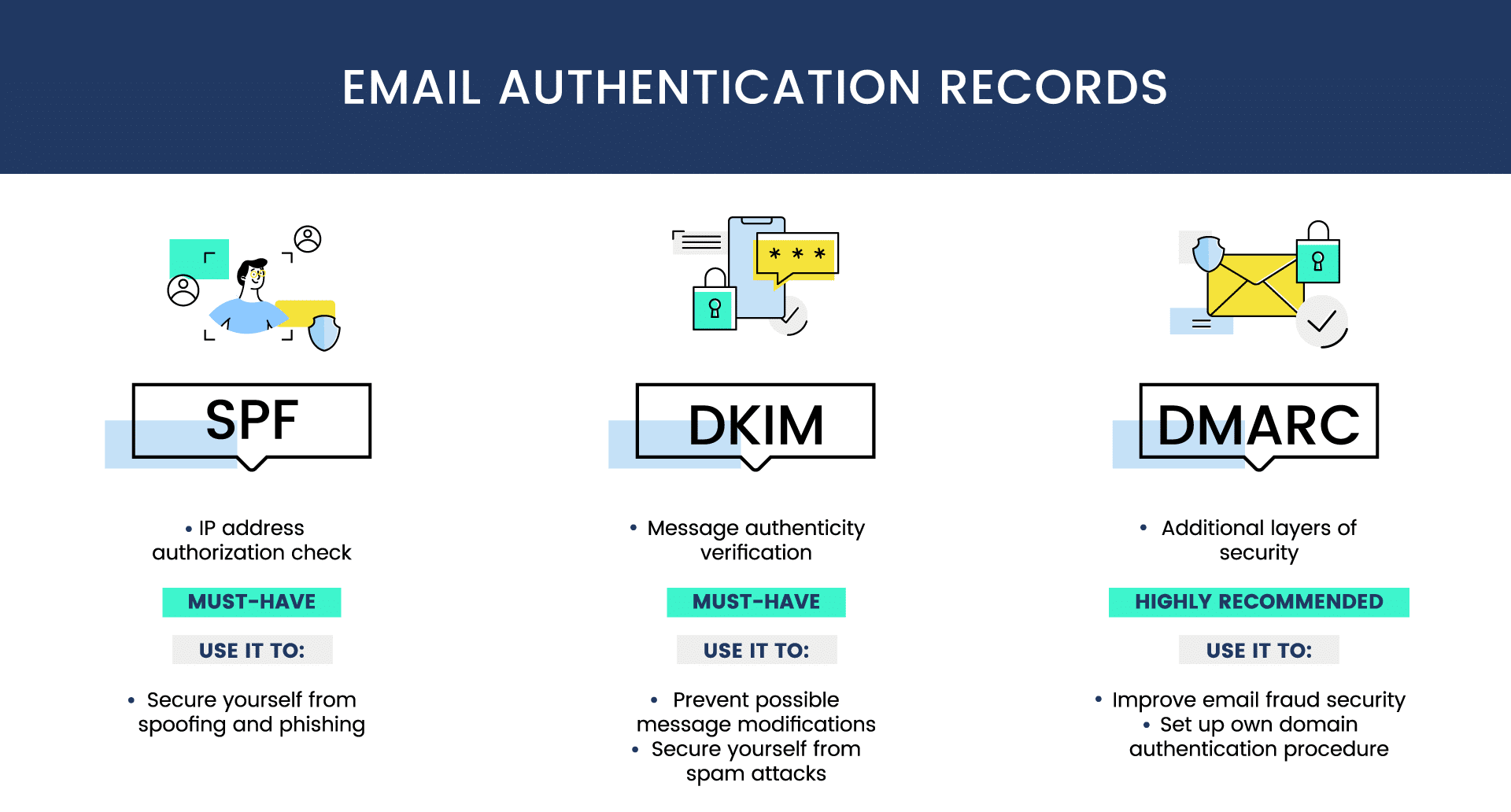
The requirements — announced by Google and Yahoo late last year — will reach much further than just e-mail marketing, thus forcing all companies to secure adoption of a trio of security technologies to catch up.
Enterprises using Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) will gain protection against impersonation through better authentication, while DMARC creates a notification channel to collect information on whether their email is being spoofed.
The trio of email security technologies have seen accelerated adoption in recent years — especially during the coronavirus pandemic, when companies were forced into remote operations. As a result, about half of email senders have a DMARC record, but only 14% have set DMARC to enforce a strict policy of quarantine or reject — widely considered the end goal, according to data from Valimail, a DMARC service provider. About half of all companies have set their DMARC record to enforce a strict policy. However, only 1% of nonprofit domains have DMARC set up
Google’s and Yahoo’s requirements are a good start, and the market is not ready for more stringent requirements
Google’s announcement, along with Yahoo’s matching move, means that DMARC adoption is no longer a suggestion, wrote Len Shneyder, vice president of industry relations at Twilio SendGrid, an email marketing service, in a blog about the news.

